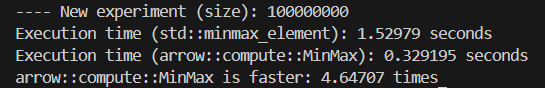
The code is looking for a min value of an array of doubles of 100M size.
The result is arrow::compute::MinMax is 3-4 times faster than std::minmax_element without noticeable memory overhead.

Programmer in Canada
The code is looking for a min value of an array of doubles of 100M size.
The result is arrow::compute::MinMax is 3-4 times faster than std::minmax_element without noticeable memory overhead.


The link to the problem https://leetcode.com/problems/divide-two-integers
What do I think about events in C#? I think they are not so different from what we have in real life. And when we have an event, we need to think of three things: who is the host, who are the guests, and what do we need to put onto the invitation cards.
Continue reading “Events in C#: Let’s Party”
Recently, I ran into an issue involving implicit type conversion. Before this case, I expected that compiler took care of any implicit conversions it allowed. Apparently, it is not true.
Continue reading “C#: Even implicit conversions of types are not safe”Sometimes we have an object which requires a Web server response to work properly. How are we gonna unit test it? Do we need an actual Web server returning all the responses we want for testing? Apparently we don’t because in .NET we can associate our requests with particular responses using WebRequest.RegisterPrefix
Continue reading “Unit Testing .NET Code That Requires Web Server Responses”Recently I was watching a very nice explanation of LSP on Christopher Okhravi’s YouTube channel. After approximately five minutes of watching this video I wanted to know one thing: how can I actually break it?
Because, you know, breaking things when you learn gives you better understanding of how they work. Am I right?
Continue reading “Breaking Bad: Liskov’s Substitution Principle (LSP) violation”Encouraged by Dmitry aka Senior Software Vlogger recently I read an interesting paper called “Out of the Tar Pit” by Ben Moseley and Peter Marks. Good 50% of the article is way over my head.
According to the paper the two most important ways of how complexity comes to our apps are State and Control. Control is order in which things happen inside app. State is variables that change what and in which order program does. Both of them make an app hard to understand hence to modify.
The less State and Control a computer program has the better. The simplest program “Hello world!” does not have State and has only one thing to do (console output of a hard-coded string).
That’s all right but the authors say that OOP (which I like a lot) does not help fighting complexity. And this conclusion surprised me because… it really does! I wanted to check the authors conclusion by practice.
Continue reading “Fighting Complexity of a Simple Calculator App”